Tkinter :
commonly comes bundled with Python, using Tk and is Python's standard GUI framework. It is famous for its simplicity and graphical user interface. It is open-source and available under the Python License.
Note : Tkinter comes pre-installed with Python3, and you need not bother about installing it.
Now, let's build a very simple GUI with the help of Tkinter and understand it with the help of a flow diagram.
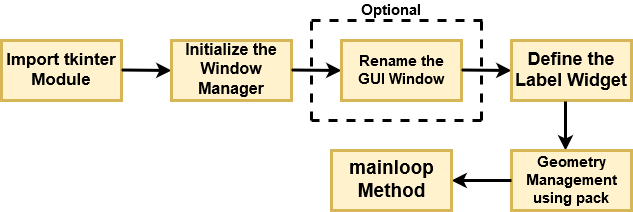
Flow Diagram for Rendering a Basic GUI
Let's break down the above flow diagram and understand what each component is handling!
- First, you import the key component, i.e., the
Tkintermodule. - As a next step, you initialize the window manager with the
tkinter.Tk()method and assign it to a variable. This method creates a blank window with close, maximize, and minimize buttons on the top as a usual GUI should have. - Then as an optional step, you will Rename the title of the window as you like with
window.title(title_of_the_window). - Next, you make use of a
widgetcalledLabel, which is used to insert some text into the window. - Then, you make use of Tkinter's
geometry managementattribute calledpack()to display the widget in size it requires. - Finally, as the last step, you use the mainloop() method to display the window until you manually close it. It runs an infinite loop in the backend.
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
# to rename the title of the window
window.title("GUI")
# pack is used to show the object in the window
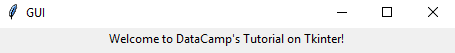
label = tkinter.Label(window, text = "Welcome to DataCamp's Tutorial on Tkinter!").pack()
window.mainloop()After running the above code in a terminal, you shall see a similar output, as shown below.
Similarly, you could have a widget Button, and the GUI will display a button instead of some text (Label).
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("Button GUI")
button_widget = tkinter.Button(window, text="Welcome to DataCamp's Tutorial on Tkinter")
button_widget.pack()
tkinter.mainloop()